背景 By 魯迅 By 高爾基 說明: 1. Kernel版本:4.14 2. ARM64處理器,Contex A53,雙核 3. 使用工具:Source Insight 3.5, Visio 1. 介紹 在 "(四)Linux記憶體模型之Sparse Memory Model" 中,我們分析了 函數 ...
背景
Read the fucking source code!--By 魯迅A picture is worth a thousand words.--By 高爾基
說明:
- Kernel版本:4.14
- ARM64處理器,Contex-A53,雙核
- 使用工具:Source Insight 3.5, Visio
1. 介紹
在(四)Linux記憶體模型之Sparse Memory Model中,我們分析了bootmem_init函數的上半部分,這次讓我們來到下半部分吧,下半部分主要是圍繞zone_sizes_init函數展開。
前景回顧:
bootmem_init()函數代碼如下:
void __init bootmem_init(void)
{
unsigned long min, max;
min = PFN_UP(memblock_start_of_DRAM());
max = PFN_DOWN(memblock_end_of_DRAM());
early_memtest(min << PAGE_SHIFT, max << PAGE_SHIFT);
max_pfn = max_low_pfn = max;
arm64_numa_init();
/*
* Sparsemem tries to allocate bootmem in memory_present(), so must be
* done after the fixed reservations.
*/
arm64_memory_present();
sparse_init();
zone_sizes_init(min, max);
memblock_dump_all();
}在Linux中,物理記憶體地址區域採用zone來管理。不打算來太多前戲了,先上一張zone_sizes_init的函數調用圖吧:
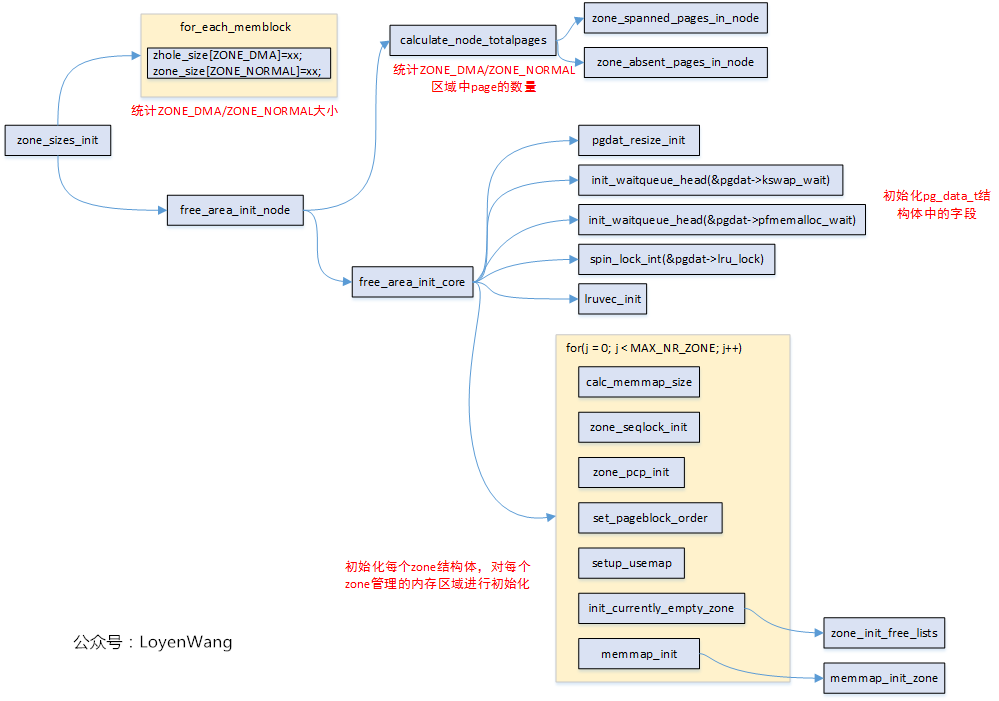
需要再說明一點是,使用的是ARM64,UMA(只有一個Node),此外,流程分析中那些沒有打開的巨集,相應的函數就不深入分析了。開始探索吧!
2. 數據結構

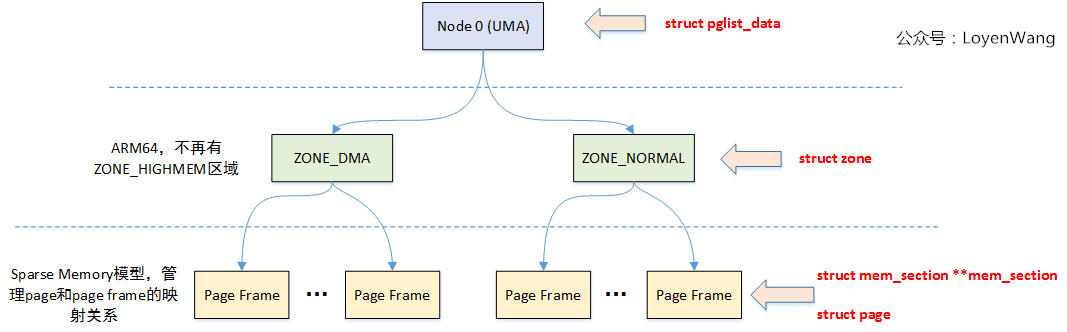
關鍵的結構體如上圖所示。
在NUMA架構下,每一個Node都會對應一個struct pglist_data,在UMA架構中只會使用唯一的一個struct pglist_data結構,比如我們在ARM64 UMA中使用的全局變數struct pglist_data __refdata contig_page_data。
struct pglist_data 關鍵欄位
struct zone node_zones[]; //對應的ZONE區域,比如ZONE_DMA,ZONE_NORMAL等
struct zonelist_node_zonelists[];
unsigned long node_start_pfn; //節點的起始記憶體頁面幀號
unsigned long node_present_pages; //總共可用的頁面數
unsigned long node_spanned_pages; //總共的頁面數,包括有空洞的區域
wait_queue_head_t kswapd_wait; //頁面回收進程使用的等待隊列
struct task_struct *kswapd; //頁面回收進程
struct zone 關鍵欄位
unsigned long watermark[]; //水位值,WMARK_MIN/WMARK_LOV/WMARK_HIGH,頁面分配器和kswapd頁面回收中會用到
long lowmem_reserved[]; //zone中預留的記憶體
struct pglist_data *zone_pgdat; //執行所屬的pglist_data
struct per_cpu_pageset *pageset; //Per-CPU上的頁面,減少自旋鎖的爭用
unsigned long zone_start_pfn; //ZONE的起始記憶體頁面幀號
unsigned long managed_pages; //被Buddy System管理的頁面數量
unsigned long spanned_pages; //ZONE中總共的頁面數,包含空洞的區域
unsigned long present_pages; //ZONE里實際管理的頁面數量
struct frea_area free_area[]; //管理空閑頁面的列表巨集觀點的描述:struct pglist_data描述單個Node的記憶體(UMA架構中的所有記憶體),然後記憶體又分成不同的zone區域,zone描述區域內的不同頁面,包括空閑頁面,Buddy System管理的頁面等。
3. zone
上個代碼吧:
enum zone_type {
#ifdef CONFIG_ZONE_DMA
/*
* ZONE_DMA is used when there are devices that are not able
* to do DMA to all of addressable memory (ZONE_NORMAL). Then we
* carve out the portion of memory that is needed for these devices.
* The range is arch specific.
*
* Some examples
*
* Architecture Limit
* ---------------------------
* parisc, ia64, sparc <4G
* s390 <2G
* arm Various
* alpha Unlimited or 0-16MB.
*
* i386, x86_64 and multiple other arches
* <16M.
*/
ZONE_DMA,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_ZONE_DMA32
/*
* x86_64 needs two ZONE_DMAs because it supports devices that are
* only able to do DMA to the lower 16M but also 32 bit devices that
* can only do DMA areas below 4G.
*/
ZONE_DMA32,
#endif
/*
* Normal addressable memory is in ZONE_NORMAL. DMA operations can be
* performed on pages in ZONE_NORMAL if the DMA devices support
* transfers to all addressable memory.
*/
ZONE_NORMAL,
#ifdef CONFIG_HIGHMEM
/*
* A memory area that is only addressable by the kernel through
* mapping portions into its own address space. This is for example
* used by i386 to allow the kernel to address the memory beyond
* 900MB. The kernel will set up special mappings (page
* table entries on i386) for each page that the kernel needs to
* access.
*/
ZONE_HIGHMEM,
#endif
ZONE_MOVABLE,
#ifdef CONFIG_ZONE_DEVICE
ZONE_DEVICE,
#endif
__MAX_NR_ZONES
};通用記憶體管理要應對各種不同的架構,X86,ARM,MIPS...,為了減少複雜度,只需要挑自己架構相關的。目前我使用的平臺,只配置了ZONE_DMA和ZONE_NORMAL。Log輸出如下圖:
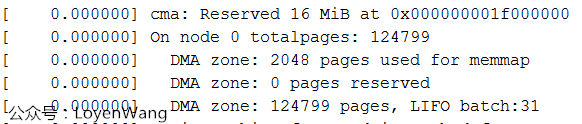
為什麼沒有ZONE_NORMAL區域內,跟蹤一通代碼發現,ZONE_DMA區域設置的大小是從起始記憶體開始的4G區域並且不能超過4G邊界區域,而我使用的記憶體為512M,所以都在這個區域內了。
從上述結構體中可以看到,ZONE_DMA是由巨集定義的,ZONE_NORMAL才是所有架構都有的區域,那麼為什麼需要一個ZONE_DMA區域內,來張圖:
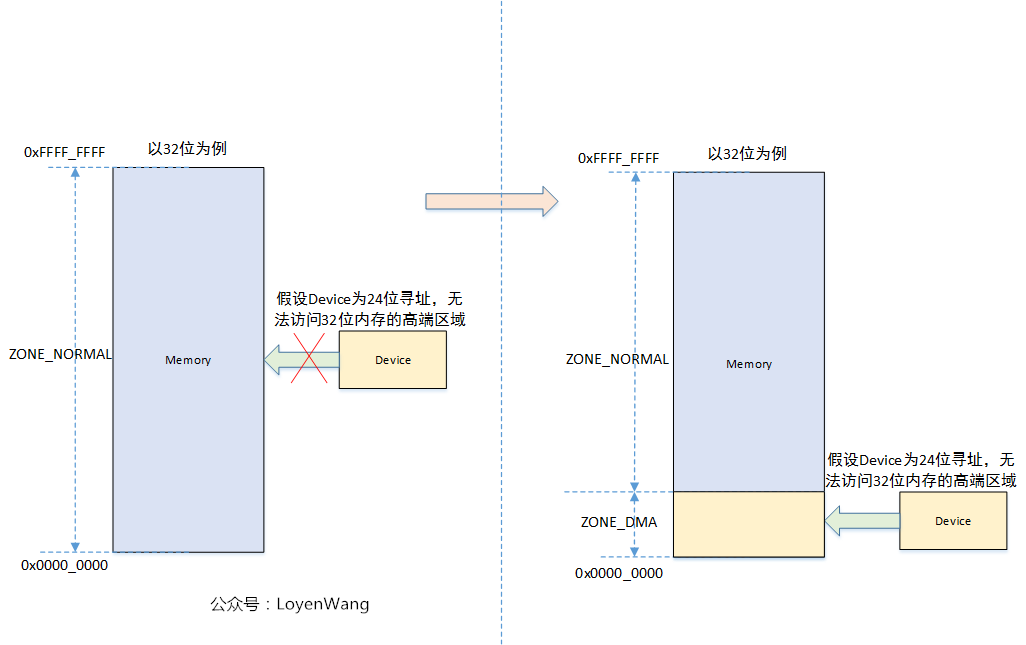
所以,如果所有設備的定址範圍都是在記憶體的區域內的話,那麼一個ZONE_NORMAL是夠用的。
4. calculate_node_totalpages
這個從名字看就很容易知道是為了統計Node中的頁面數,一張圖片解釋所有:
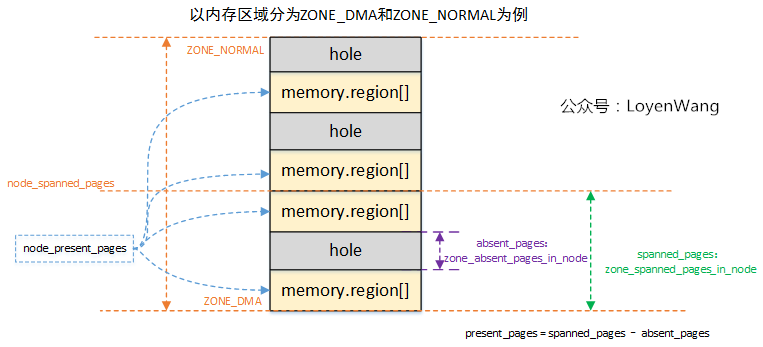
- 前邊的文章分析過,物理記憶體由
memblock維護,整個記憶體區域,是有可能存在空洞區域,也就是圖中的hole部分; - 針對每個類型的
ZONE區域,分別會去統計跨越的page frame,以及可能存在的空洞,並計算實際可用的頁面present_pages; Node管理各個ZONE,它的spanned_pages和present_pages是統計各個ZONE相應頁面之和。
這個過程計算完,基本就把頁框的信息納入管理了。
5. free_area_init_core
簡單來說,free_area_init_core函數主要完成struct pglist_data結構中的欄位初始化,並初始化它所管理的各個zone,看一下代碼吧:
/*
* Set up the zone data structures:
* - mark all pages reserved
* - mark all memory queues empty
* - clear the memory bitmaps
*
* NOTE: pgdat should get zeroed by caller.
*/
static void __paginginit free_area_init_core(struct pglist_data *pgdat)
{
enum zone_type j;
int nid = pgdat->node_id;
pgdat_resize_init(pgdat);
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA_BALANCING
spin_lock_init(&pgdat->numabalancing_migrate_lock);
pgdat->numabalancing_migrate_nr_pages = 0;
pgdat->numabalancing_migrate_next_window = jiffies;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_TRANSPARENT_HUGEPAGE
spin_lock_init(&pgdat->split_queue_lock);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&pgdat->split_queue);
pgdat->split_queue_len = 0;
#endif
init_waitqueue_head(&pgdat->kswapd_wait);
init_waitqueue_head(&pgdat->pfmemalloc_wait);
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPACTION
init_waitqueue_head(&pgdat->kcompactd_wait);
#endif
pgdat_page_ext_init(pgdat);
spin_lock_init(&pgdat->lru_lock);
lruvec_init(node_lruvec(pgdat));
pgdat->per_cpu_nodestats = &boot_nodestats;
for (j = 0; j < MAX_NR_ZONES; j++) {
struct zone *zone = pgdat->node_zones + j;
unsigned long size, realsize, freesize, memmap_pages;
unsigned long zone_start_pfn = zone->zone_start_pfn;
size = zone->spanned_pages;
realsize = freesize = zone->present_pages;
/*
* Adjust freesize so that it accounts for how much memory
* is used by this zone for memmap. This affects the watermark
* and per-cpu initialisations
*/
memmap_pages = calc_memmap_size(size, realsize);
if (!is_highmem_idx(j)) {
if (freesize >= memmap_pages) {
freesize -= memmap_pages;
if (memmap_pages)
printk(KERN_DEBUG
" %s zone: %lu pages used for memmap\n",
zone_names[j], memmap_pages);
} else
pr_warn(" %s zone: %lu pages exceeds freesize %lu\n",
zone_names[j], memmap_pages, freesize);
}
/* Account for reserved pages */
if (j == 0 && freesize > dma_reserve) {
freesize -= dma_reserve;
printk(KERN_DEBUG " %s zone: %lu pages reserved\n",
zone_names[0], dma_reserve);
}
if (!is_highmem_idx(j))
nr_kernel_pages += freesize;
/* Charge for highmem memmap if there are enough kernel pages */
else if (nr_kernel_pages > memmap_pages * 2)
nr_kernel_pages -= memmap_pages;
nr_all_pages += freesize;
/*
* Set an approximate value for lowmem here, it will be adjusted
* when the bootmem allocator frees pages into the buddy system.
* And all highmem pages will be managed by the buddy system.
*/
zone->managed_pages = is_highmem_idx(j) ? realsize : freesize;
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA
zone->node = nid;
#endif
zone->name = zone_names[j];
zone->zone_pgdat = pgdat;
spin_lock_init(&zone->lock);
zone_seqlock_init(zone);
zone_pcp_init(zone);
if (!size)
continue;
set_pageblock_order();
setup_usemap(pgdat, zone, zone_start_pfn, size);
init_currently_empty_zone(zone, zone_start_pfn, size);
memmap_init(size, nid, j, zone_start_pfn);
}
}- 初始化
struct pglist_data內部使用的鎖和隊列;
遍歷各個zone區域,進行如下初始化:
根據
zone的spanned_pages和present_pages,調用calc_memmap_size計算管理該zone所需的struct page結構所占的頁面數memmap_pages;zone中的freesize表示可用的區域,需要減去memmap_pages和DMA_RESERVE的區域,如下圖在開發板的Log列印所示:memmap使用2048頁,DMA保留0頁;
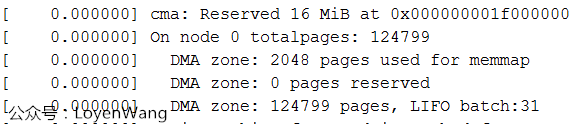
計算
nr_kernel_pages和nr_all_pages的數量,為了說明這兩個參數和頁面的關係,來一張圖(由於我使用的平臺只有一個ZONE_DMA區域,且ARM64沒有ZONE_HIGHMEM區域,不具備典型性,故以ARM32為例):
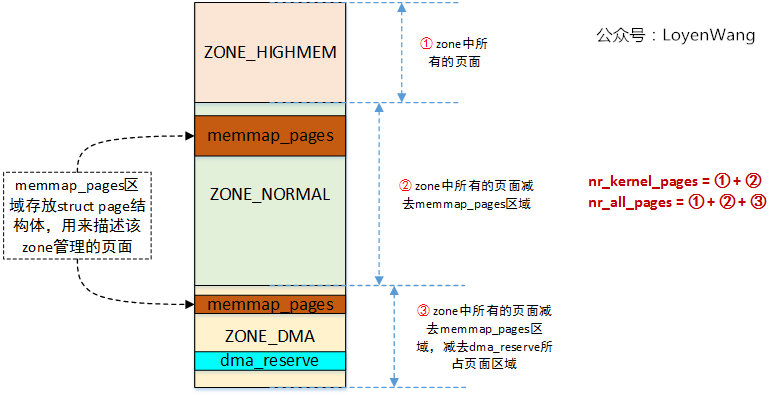
初始化
zone使用的各類鎖;分配和初始化
usemap,初始化Buddy System中使用的free_area[],lruvec,pcp等;memmap_init()->memmap_init_zone(),該函數主要是根據PFN,通過pfn_to_page找到對應的struct page結構,並將該結構進行初始化處理,並設置MIGRATE_MOVABLE標誌,表明可移動;
最後,當我們回顧bootmem_init函數時,發現它基本上完成了linux物理記憶體框架的初始化,包括Node, Zone, Page Frame,以及對應的數據結構等。
結合上篇文章(四)Linux記憶體模型之Sparse Memory Model閱讀,效果會更佳噢!
持續中...




